Sorry kalau ada formatting aneh… dari word ke blog.
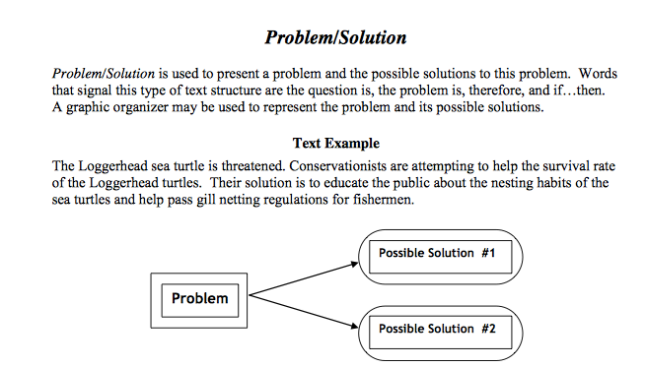
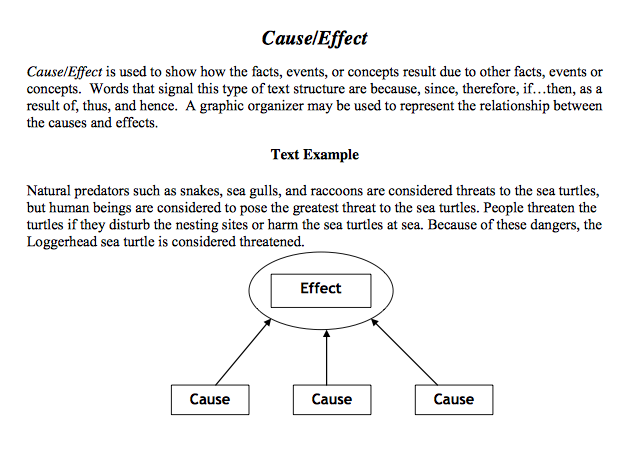
Menganalisis Paragraf
Paragraf
- Kumpulan kalimat
- Mengandung ide pokok
- (setiap paragraf baru) ditulis pada baris baru, ada yang menjorok
- Bagian dari bacaan
- Disebut juga alinea
- Dibedakan menjadi induktif dan deduktif
- Idealnya kohesif dan koheran
- Kohesif: bahasanya menyatu (menggunakan konjungsi)
- Koheren: maknanya padu (menggunakan repetisi)
Komposisi Paragraf
- Topik (subtopik/topik kecil)
- Gagasan/ide pokok dan pendukung
- Kalimat utama dan penjelas
|
Deduktif |
Induktif |
|
|
Menganalisis Paragraf
| Topik kecil | Hal yang dibicarakan, subjeknya, bersifat nominal, bisa menjadi pertanyaan
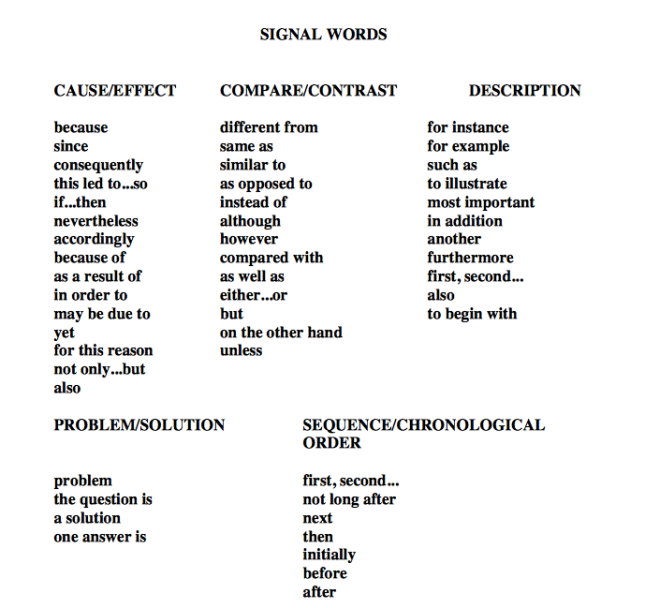
Untuk menentukan topik dapat menggunakan kata penghubung yaitu:
|
| Kalimat Utama | Kalimat pertama |
| Gagasan Utama | Ide-ide pembicaraan, subjek + predikat, bersifat verbal, kurang lebih sama dengan kalimat utama
Subtopik + kata kunci |
| Kata kunci | Jawaban dari topik kecil, adalah predikat (kata kerja, kata sifat, kata bilangan atau kata benda) dari kalimat utama |
| Jenis paragraf | Induktif atau deduktif |
Menulis Cerita Pendek
Cerpen:
Fokus pada satu tokoh, satu permasalahan, satu latar, satu konflik -> pendek
Dimensi Cerpen
- Tema
- Moral
- Tokoh Utama
- Alur
- Latar tempat, waktu, dan budaya
Majas
- Hiperbola: melebih-lebihkan
- Litotes: merendah-rendahkan
- Metafora: kiasan
- Repetisio: mengulang-ulang
- Personifikasi: memberi hidup pada benda mati
- Simile: membandingkan dengan kata seperti, layaknya, laksana
- Elispsis: Satu kata dalam satu kalimat
- Retorik: pertanyaan tak berjawaban
- Ironi: sindiran
- Sarkasme: menyindir, mengejek
Teks Iklan
Sifat Bahasa Iklan
- Persuasif
- Subjektif
- Menggoda, provokatif
- Opini > Fakta
- Hiperbolis
- Singkat
- Deskriptif
- Tidak baku
- Komunikatif
- Ambigu
Kata-kata opini
- Kata sifat -> sangat, sekali, lebih
- Menurut
- Se-nya
- Mungkin, agaknya, kalau tidak salah
- Pasti
- Hanya
Kata-kata fakta
- Kata bilangan
- Ukuran/dimensi
- Spesifikasi
- Pelaku (oleh)
- Waktu (pada)
- Tempat (di)
Kalimat
(Huruf kapital – subjek – predikat – titik)
Menyimak Dialog Interaktif
Pertanyaan adalah topik.
Membuat tanggapan: saya kagum… saya setuju…. saya berharap….
Reportase
Umum ke khusus
Kata yang Sering Digunakan
- Pemirsa
- Sekarang saya sedang berada di….
- Seperti telah diketahhui, di sini (telah, baru saja, sedang) terjadi…
- Seperti dapat dilihat di sini/di layar kaca Anda..
- Dapat kini sampaikan / laporkan bahwa…
- Dari informasi yang berhasil kami kumpulkan/ catatan yang kami miliki
- Oleh sebab itu kami menghimbau/menyarankan
| SALAM PEMBUKA | Selamat sore, pemirsa | |
| PEMBUKA | WHERE | Permirsa, sekarang saya berada di |
| WHAT | Pemirsa, seperti telah diketahui/ terlihat di layar kaca, di sini baru saja terjadi | |
| INTI | ||
| FOKUS 1 | WHY | Pemirsa, dari informasi yang berhasil kami kumpulkan, kebakaran ini diduga disebabkan oleh |
| FOKUS 2 | WHEN | Pemirsa, menurut saksi mata, kebakaran ini pertama kali diketahui terjadi pada pukul 13.30 (pada saat sebagian warga tidak ada dirumah karena pergi bekerja ). |
| FOKUS 3 | WHO | ( saksi pelaku /tidak sengaja) |
| (saksi ahli) | ||
| (saksi korban) | ||
| Untuk mengetahui lebih jauh apa yang terjadi, sekarang Bapak Ronald sudah ada di samping saya.
REPORTER = NARA SUMBER = |
||
| FOKUS 4 | HOW 1 – mengatasinya? | (Upaya warga)
(Upaya pemerintah) |
| HOW 2 – hambatannya? | Faktor cuaca….
Faktor lokasi yg sempit…. Faktor pemicu |
|
| HOW 3 – sikap /reaksi warga | ||
| HOW 4 – tanggapan pemerintah | mengevakuasi | |
| HOW 5 – kerugian | (jiwa) (luka-luka, meninggal, cacat, dsb)
(material) -322 rumah hangus (social) (tidak bisa bersekolah, kehilangan tempat tinggal, kehilangan pekerjaan, dsb) |
|
| PENUTUP | PERNYATAAN SELESAI | Demikian informasi yang dapat kami sampaikan…. |
| OPINI | Oleh sebab itu kami menghimbau/enyarankan… | |
| NAMA, TV | Saya Aitya Wisnu, TV One | |
| LOKASI SIARAN | Melaporkan dari lokasi kejadian. Dan kita kembali ke studio. | |
Menulis Surat Pembaca
- 3 Paragraf: fakta, opini, saran
Kerangka
- Fakta/ latar belakang kejadian (4 W – tdk ada why)
- Hal yang dipersoalkan
- Opini/tanggapan terhadap persoalan
- Alasan dan argumen
- Pihak yang dipersoalkan
- Tuntutan
- Saran
Menyunting
- Judul
- Surat pembaca: tidak ke[an, -nya, yang
- Huruf kapital kecuali ke, yang, dari, untuk
- Ejaan
- Huruf besar, tanda baca
- Tulisan cetak miring untuk bahasa ingrgis
- Pemenggalan kata depan dan awalan (di + spasi kalau tempat, sambung kalau kata kerja)
- Diksi
- efektivitas
- Struktur
- Judul
- Teks: pembuka, inti, penutup
- Penutup: nama, alamat lengkap
- Isi
- Valid
- Aktual
- bermanfaat
Kata Baku Tak Baku